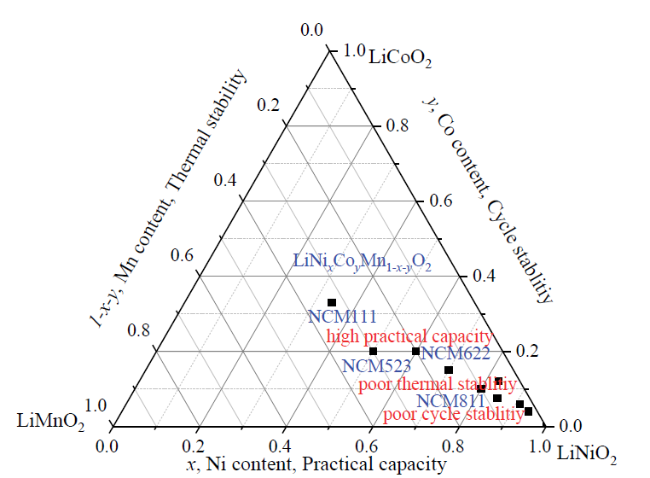
0 引言
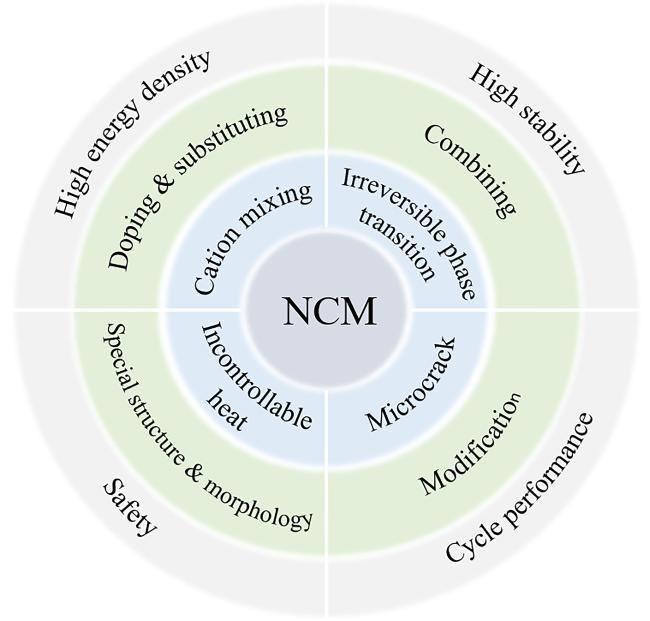
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the relation and interactions between different components in NCM图1 NCM中不同成分间的关系及相互影响示意图 |
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of the improvement of NCM图2 NCM改性示意图 |
1 NCM材料存在的问题
1.1 阳离子混排
1.2 不可逆相变
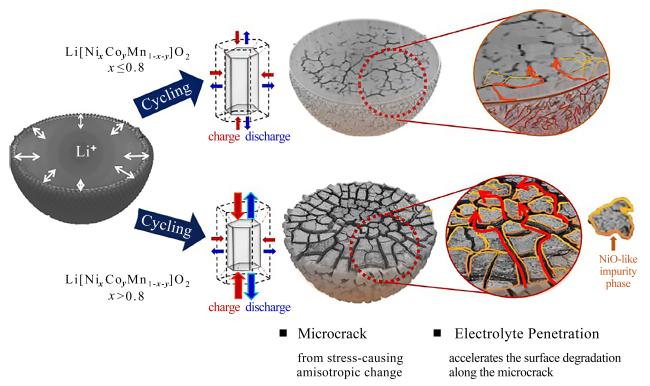
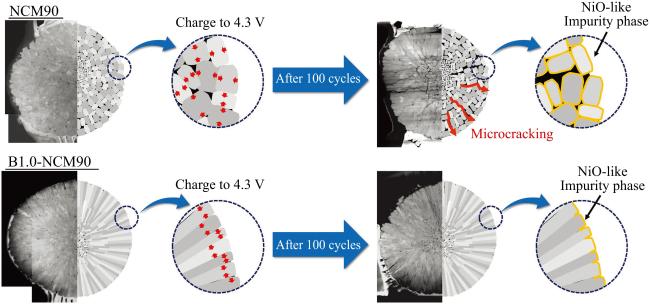
1.3 微裂纹
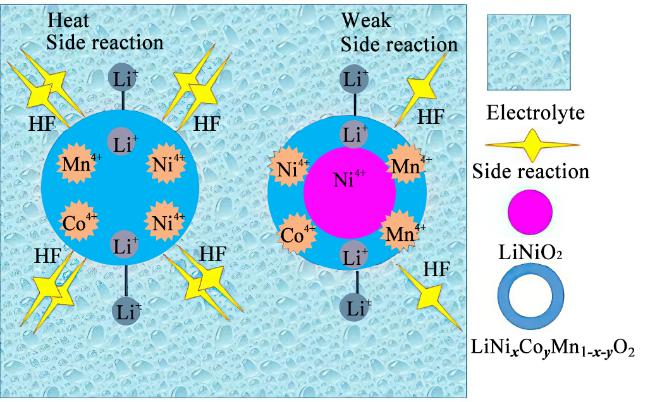
1.4 热失控
2 NCM电极材料的改性
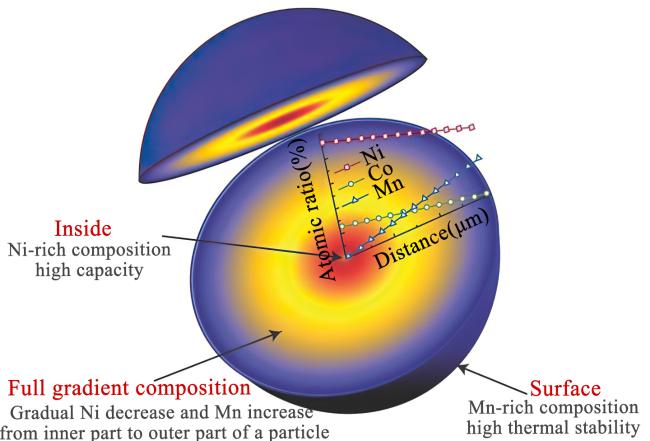
2.1 特殊结构或形貌改性
2.2 掺杂或替代改性
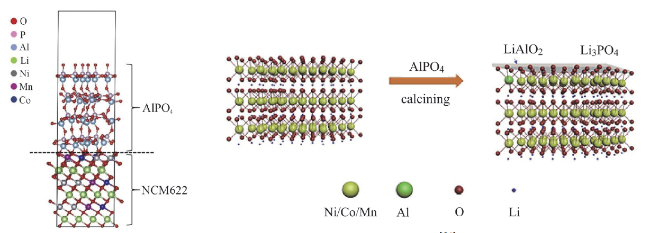
2.3 修饰改性
2.4 复合改性
3 不同改性方法的比较
Table 1 Comparisons of different improving methods for NCM materials.表1 NCM材料改性方法比较 |
| Methods | Main elements | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Special structure or morphology | Li, Ni, Co, Mn | No other foreign elements or materials, the purification of NCM electrode materials, facile preparation and control | The composition of the core and shell varies greatly, separation of core and shell, component mutation of transition metals |
| Doping or substituting | Mg, Al, Ti, Ta, W, Zr, Nb, Si, B, F | High capacity and cycle stability, improved crystal structure or size, many available elements, low cost | Some doping or substitution elements have no electrochemical activities, the first discharge specific capacity of the battery may decrease slightly with the increase of doping amount |
| Modification | Zr, W, Al, Ti, V, Fe | Excellent capacity retention during cycles, isolated from an external environment like an electrolyte, improved safety of electrode materials | Low coulombic efficiency, irreversible capacity loss during the first cycle, the unprecise distribution or control of modified materials, possible increase of cost |
| Combining | Mg, Zr, Ti, Co, F | Combined the advantages of each method or material, excellent improved whole performance | The reasonable adjustment of different methods or materials are difficult due to their complexity |