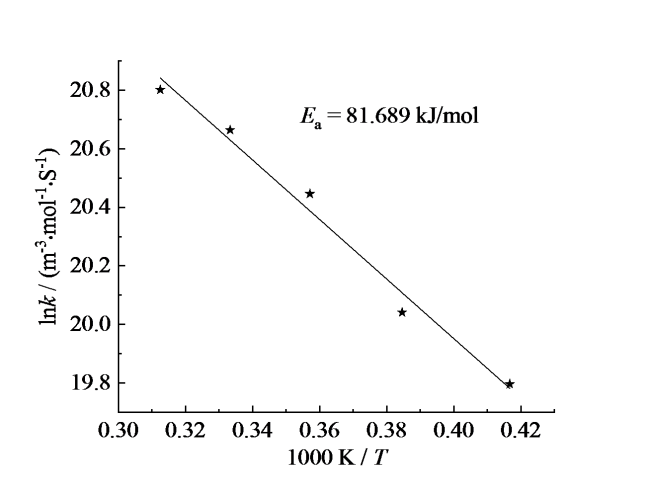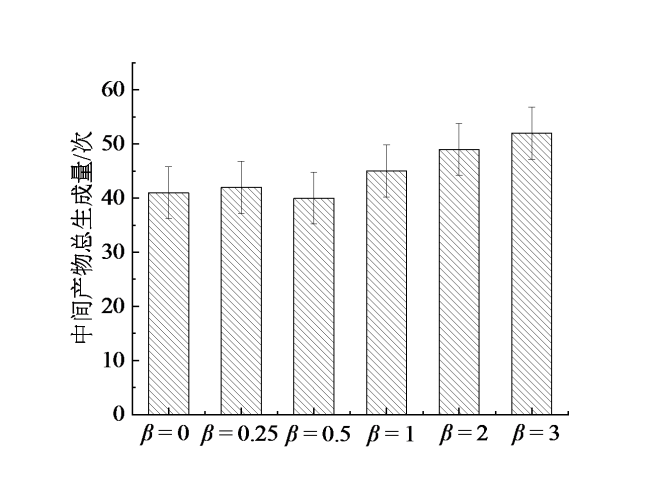0 引言
1 研究方法
1.1 反应力场分子动力学原理
1.2 案例设置
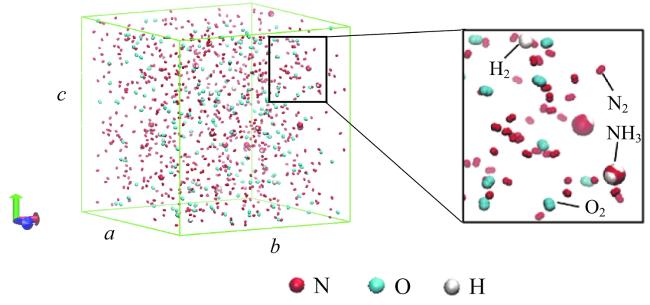
Fig. 1 A typical initial configuration of the simulation system图1 一种典型的模拟体系初始构型 |
1.3 模拟参数设置
2 结果与讨论
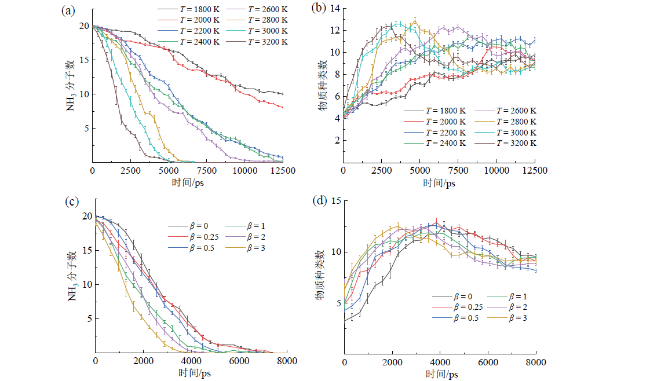
2.1 温度和燃料配比对NH3/H2燃烧反应的影响
Fig. 2 Time evolutions of NH3 consumption (a) and intermediates (b) under different temperatures; time evolutions of NH3 consumption (c) and intermediates (d) under different fuel ratios图2 不同温度下NH3的消耗规律(a)和中间产物种类随时间变化规律(b);不同燃料配比下NH3的消耗规律(c)和中间产物种类变化规律(d) |
2.2 反应活化能计算
Fig. 3 lnk-1/T curve of NH3 consumption reaction with H2 (β = 0.5)图3 加入H2(β = 0.5)的NH3消耗反应lnk-1/T曲线 |
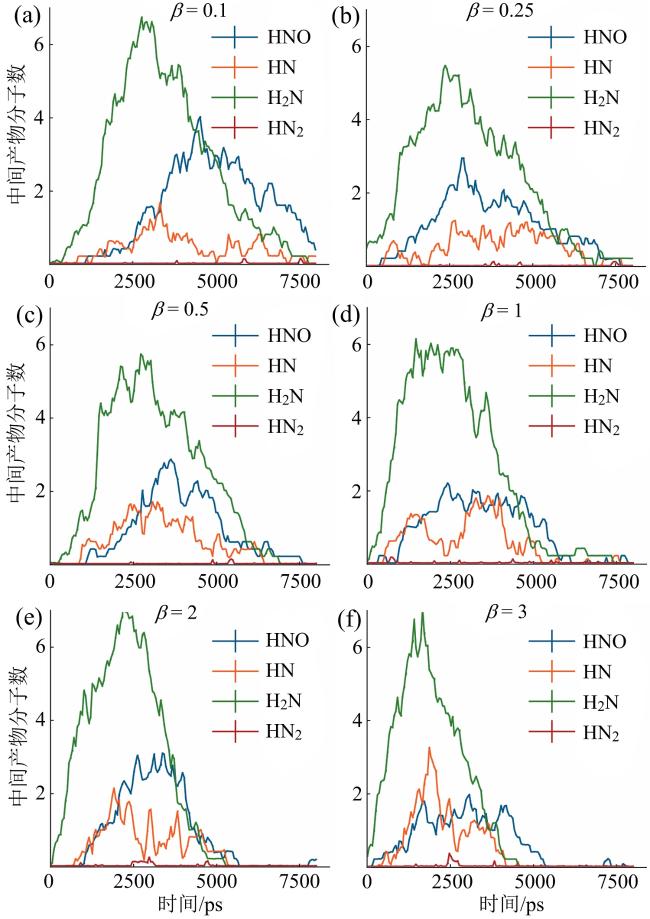
2.3 H2对主要含氮中间产物的影响
Fig. 4 Total yield of intermediate products (HN, HNO, HN2, H2N) at different fuel ratios图4 不同燃料配比下中间产物(HN、HNO、HN2、H2N)总生成次数 |
Fig. 5 Time evolutions of numbers of key nitrogen-containing intermediates under different fuel ratios图5 不同燃料配比下主要含氮中间产物数量随时间的变化 |
2.4 H2对NOx生成的影响
Fig. 6 Yields of NOx under different fuel ratios图6 不同燃料配比下NOx生成量 |
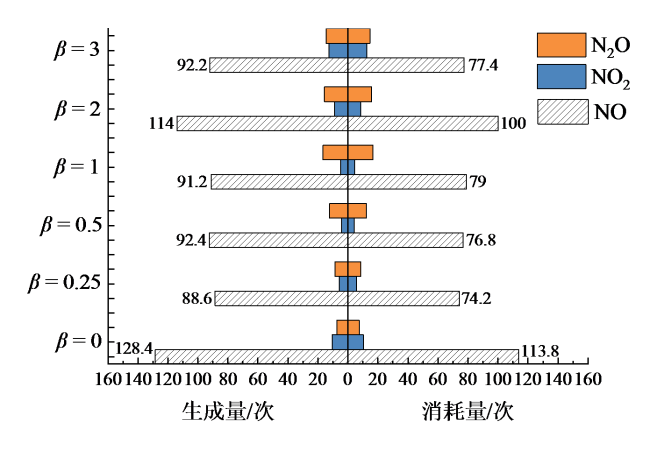
Fig. 7 Number of molecules produced and consumed by NO, NO2 and N2O under different fuel ratios图7 不同燃料配比下NO、NO2、N2O生成和消耗分子数 |
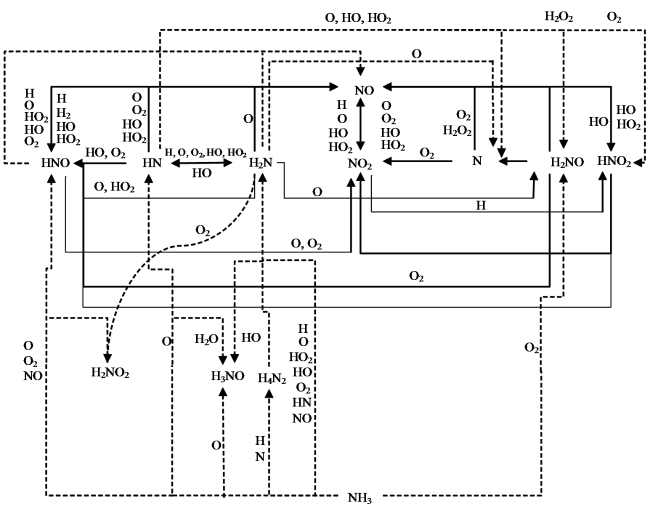
Fig. 8 Reaction pathways leading to the formation of NOx图8 NOx生成路径 |
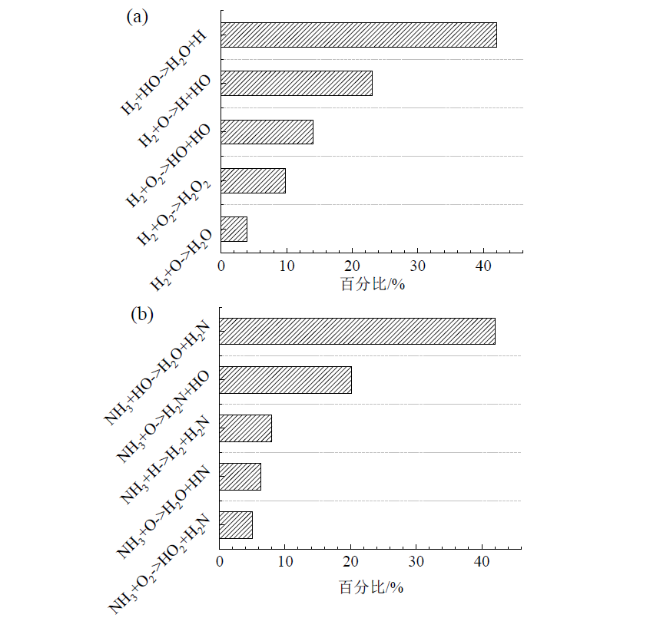
Fig. 9 Major elementary reaction pathways and percentage of all reactions occurrence frequency for H2 (a) and NH3 (b) in NH3/H2/air combustion图9 NH3/H2/空气燃烧中H2(a)和NH3(b)参与的主要基元反应路径及其所有反应发生频次的百分比 |