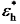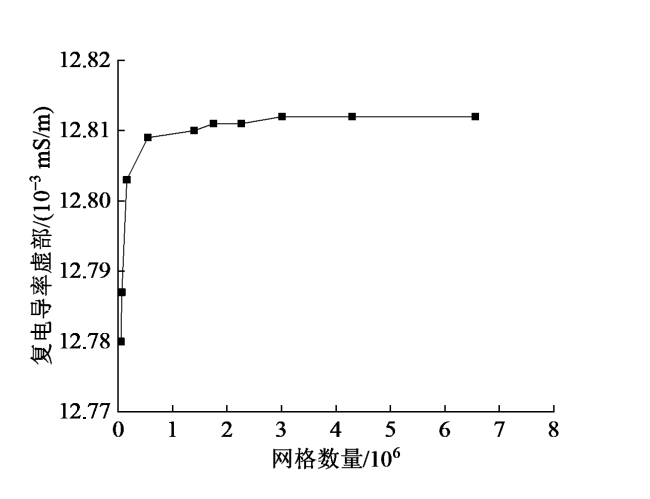0 引言
1 基本理论
1.1 复电导率和复介电常数
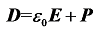
 为真空中介电常数,
为真空中介电常数,  = 8.854 × 10-12 F/m;P代表介质材料的电极化。对于时谐电场E = E0eiωt(E0表示电场强度的幅值和方向,ω为电场频率,i为虚数单位,t为时间),利用麦克斯韦方程和欧姆定律可以将总电流密度(Jt)表示为式(2)。
= 8.854 × 10-12 F/m;P代表介质材料的电极化。对于时谐电场E = E0eiωt(E0表示电场强度的幅值和方向,ω为电场频率,i为虚数单位,t为时间),利用麦克斯韦方程和欧姆定律可以将总电流密度(Jt)表示为式(2)。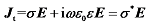
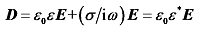
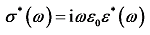
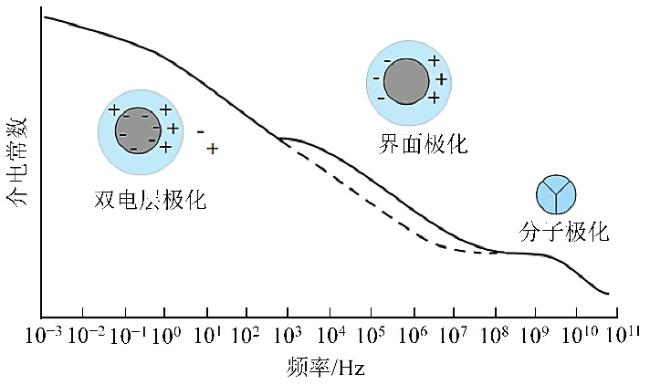
1.2 宽频电极化
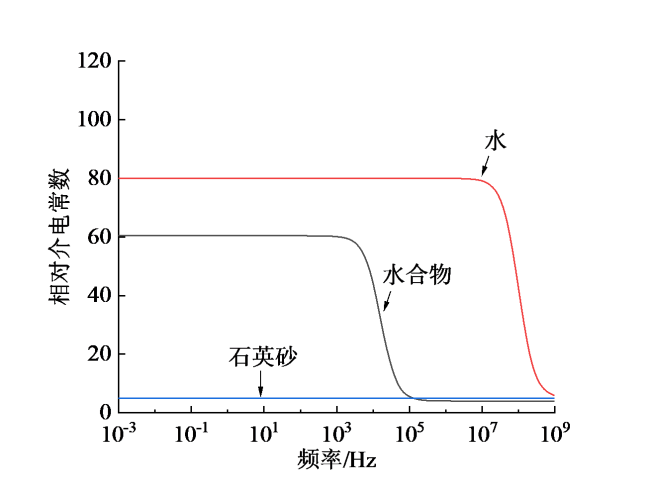
1.3 电学混合模型
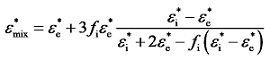
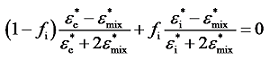
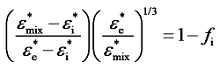
2 含水合物多孔介质有限元数值模型
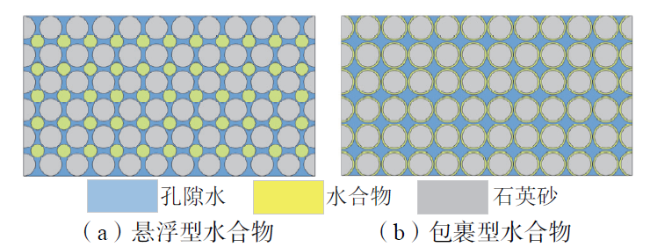
2.1 几何结构
Fig. 3 Two-dimensional model geometries of porous media图3 二维多孔介质几何结构 |
2.2 材料属性
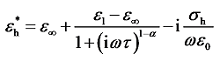
2.3 控制方程及边界条件
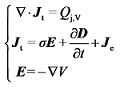
2.4 网格剖分及依赖性检验
Fig. 4 Variation curves of the imaginary part of complex conductivity of water saturated porous medium with the number of mesh cells图4 水饱和多孔介质复电导率虚部随网格数量的变化曲线 |
3 水合物饱和度和微观赋存模式对电频谱的影响
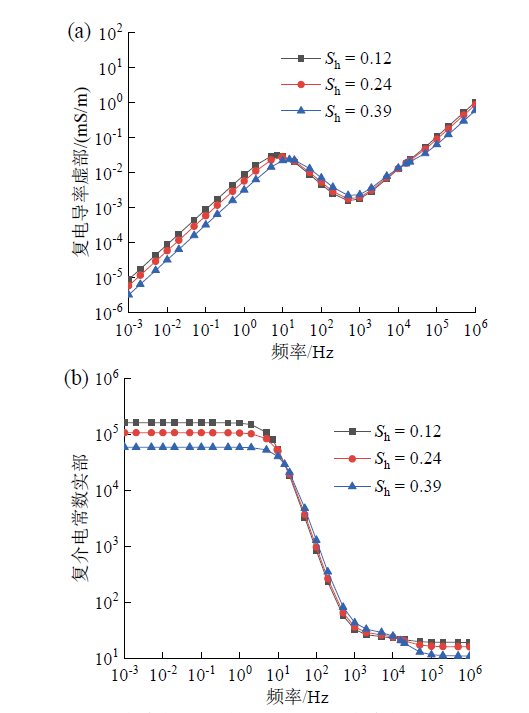
Fig. 5 Electrical frequency spectra of porous media containing suspending hydrates with different saturations: (a) imaginary part of complex conductivity; (b) real part of complex dielectric permittivity图5 不同水合物饱和度下含悬浮型水合物多孔介质电频谱:(a)复电导率虚部;(b)复介电常数实部 |
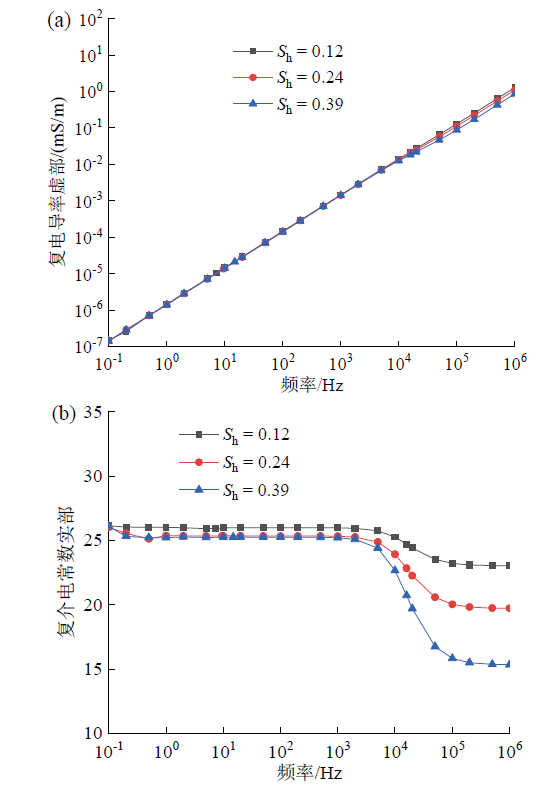
Fig. 6 Electrical frequency spectra of porous media containing coating hydrates with different saturations: (a) imaginary part of complex conductivity; (b) real part of complex dielectric permittivity图6 不同水合物饱和度下含包裹型水合物多孔介质电频谱:(a)复电导率虚部;(b)复介电常数实部 |
4 水合物饱和度计算模型
4.1 模型建立和评价方法
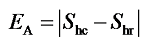
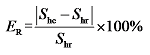
4.2 含悬浮型水合物多孔介质
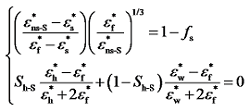
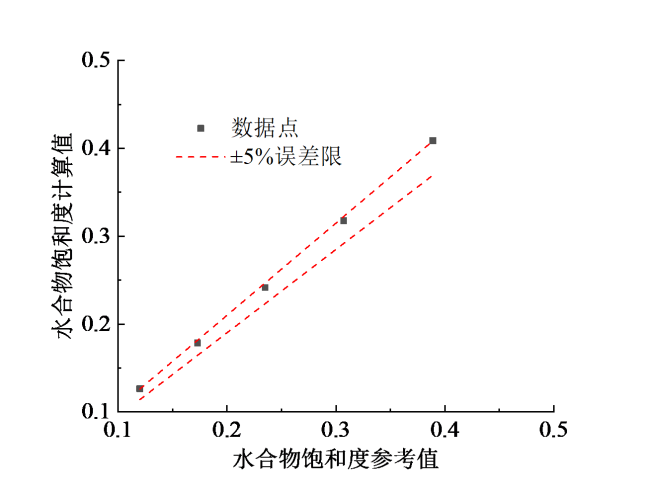
Fig. 7 Comparison between model predicted and reference hydrate saturations for suspending hydrates图7 悬浮型水合物饱和度的模型计算值与参考值的比较 |
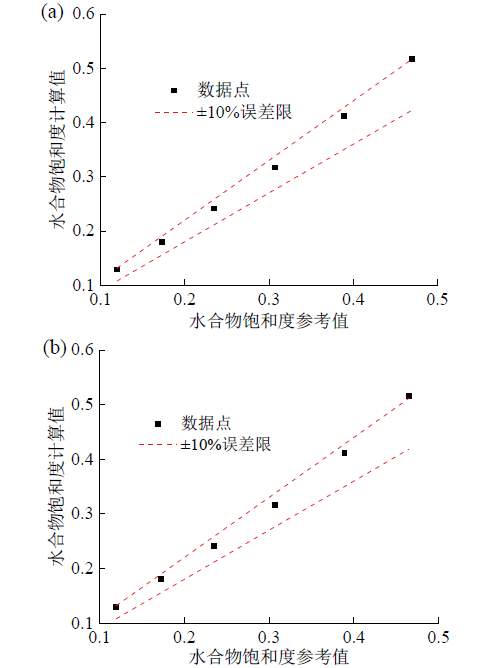
4.3 含包裹型水合物多孔介质
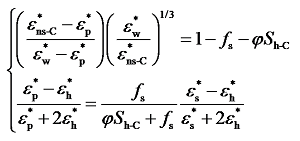
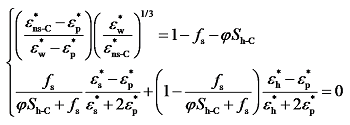
Fig. 8 Comparison between model predicted and reference hydrate saturations for coating hydrates: (a) MG-BH dielectric mixing model; (b) BR-BH dielectric mixing model图8 包裹型水合物饱和度的模型计算值与参考值的比较:(a)MG-BH介电混合模型;(b)BR-BH介电混合模型 |