0 引言
1 基于激电法评价渗透率基本原理
1.1 多孔介质复电导率与渗透率
1.2 多孔介质渗透率计算模型
2 含水合物沉积物电场和流场数值模型建立
2.1 数值建模方案
2.2 几何结构与材料参数
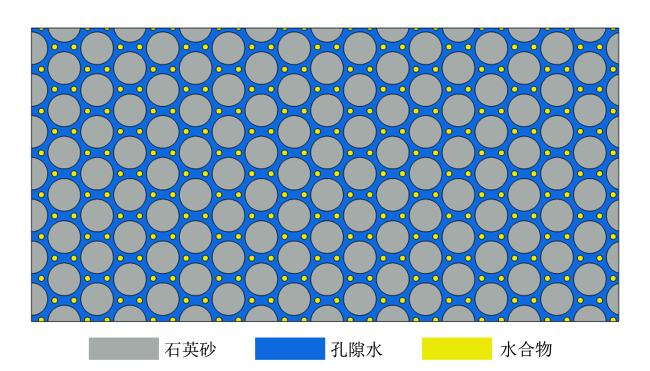
Fig. 1 Two-dimensional model geometry of a porous medium图1 二维多孔介质几何结构 |
2.3 流场/电场控制方程及边界条件
2.4 网格剖分与数值求解
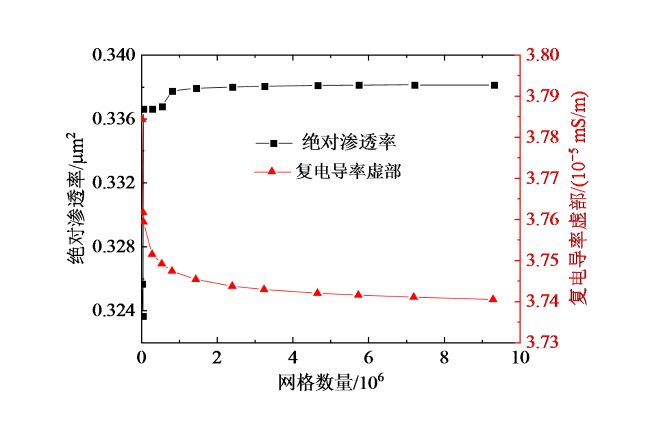
Fig. 2 Variation curves of the imaginary part of complex conductivity and absolute permeability with the number of meshes in numerical models图2 复电导率虚部和绝对渗透率随数值模型网格单元数量的变化曲线 |
3 含水合物多孔介质渗透率评价模型建立
3.1 石英砂粒径对复电导率/渗透率影响
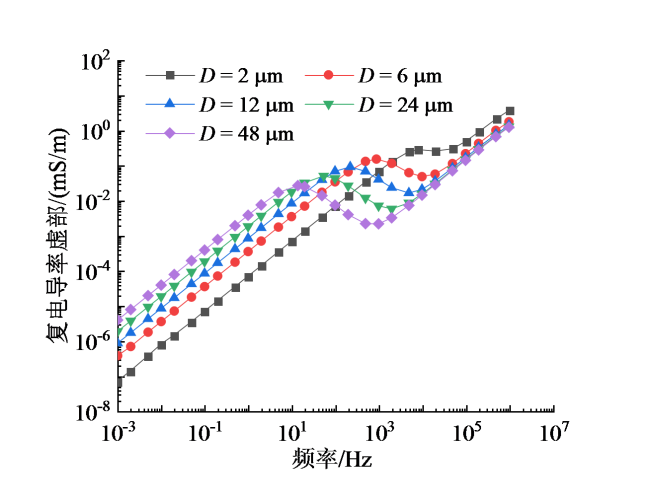
Fig. 3 Frequency dispersion curves of the imaginary part of complex conductivity for different particle sizes of quartz sands图3 石英砂粒径不同时复电导率虚部频散曲线 |
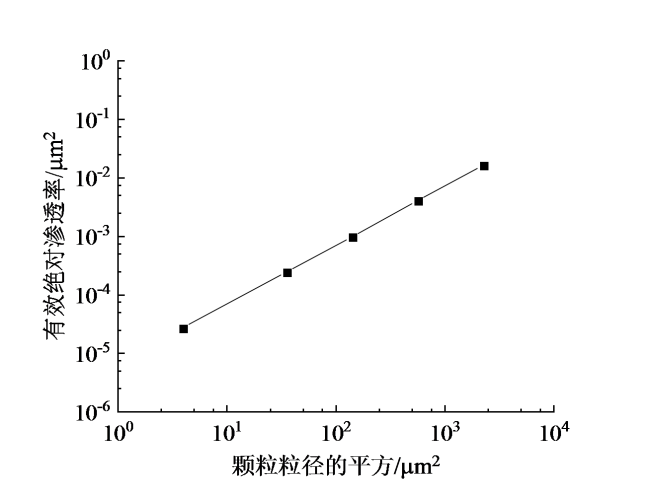
Fig. 4 Variation trend of the effective absolute permeability with grain size of quartz sands图4 有效绝对渗透率随石英砂颗粒粒径的变化趋势 |
3.2 水合物饱和度对复电导率/渗透率影响
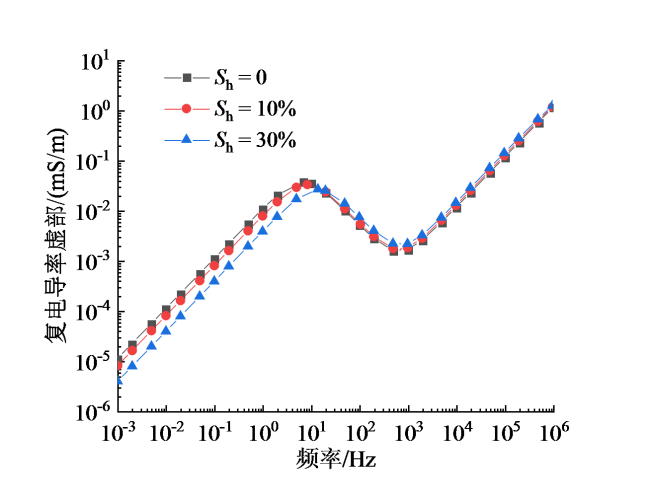
Fig. 5 Frequency dispersion curves of the imaginary part of complex conductivity for different hydrate saturations图5 水合物饱和度不同时复电导率虚部的频散曲线 |
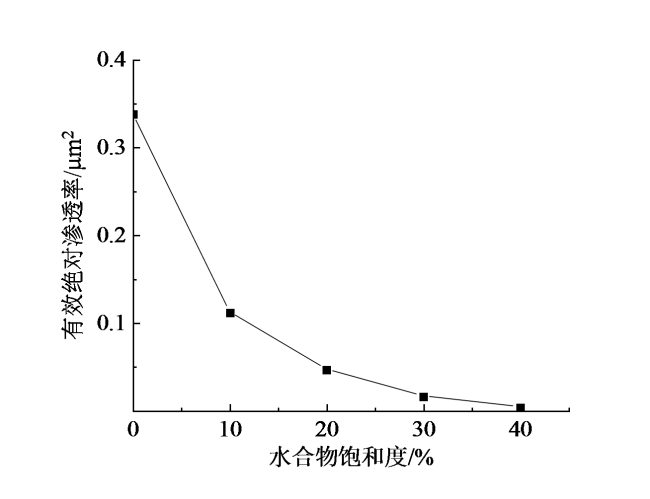
Fig. 6 Effective absolute permeability curves for different hydrate saturations图6 水合物饱和度不同时有效绝对渗透率曲线 |
3.3 基于复电导率的渗透率评价模型
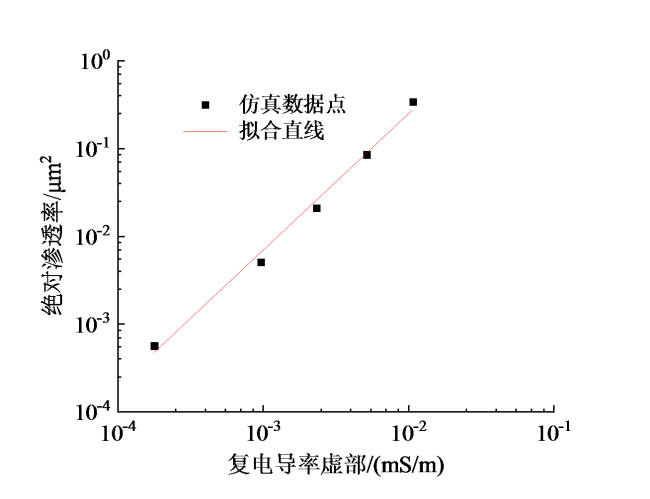
Fig. 7 Relationship between the absolute permeability and imaginary part of complex conductivity for porous media图7 多孔介质绝对渗透率与复电导率虚部的关系 |
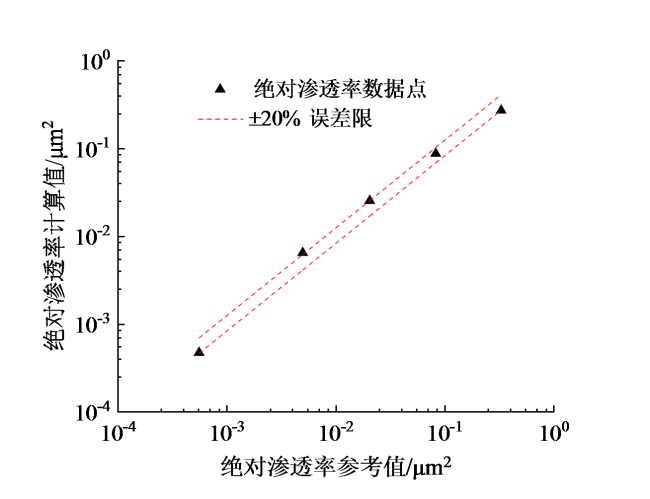
Fig. 8 Calculation results from the absolute permeability model based on the imaginary part of complex conductivity图8 基于复电导率虚部的绝对渗透率模型计算结果 |
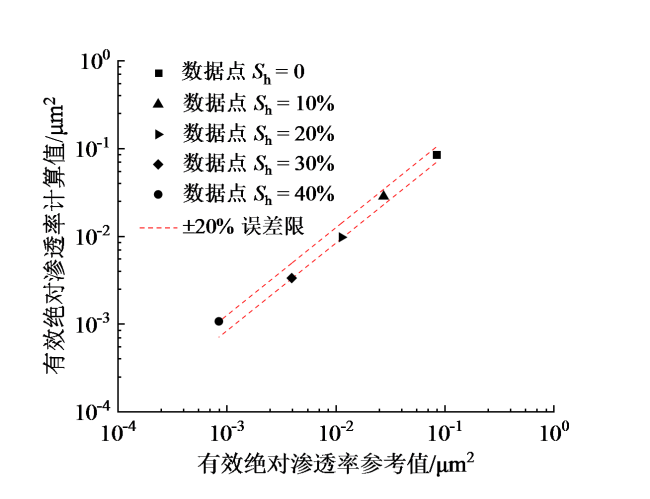
Fig. 9 Calculation results from the effective absolute permeability model based on the imaginary part of complex conductivity图9 基于复电导率虚部的有效绝对渗透率模型计算结果 |