0 引言
1 扩散层重建方法
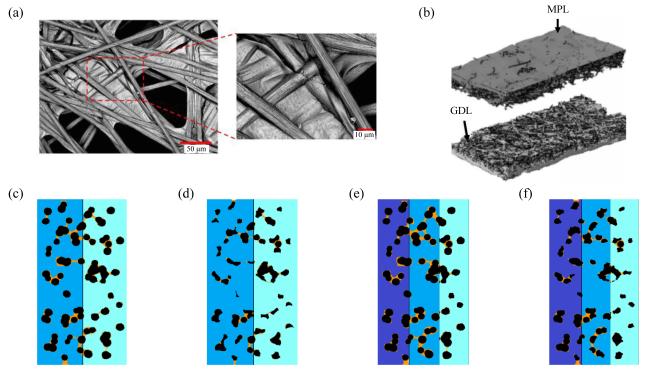
Fig. 1 GDL microstructure under CLSM (a) and 3D-X-ray tomography (b); two-dimensional microstructure of gradient diffusion layer and aging final diffusion layer (c-f)图1 CLSM(a)和3D-X射线断层扫描(b)下的GDL微观结构;梯度化扩散层及老化最终扩散层二维微观结构(c ~ f) |
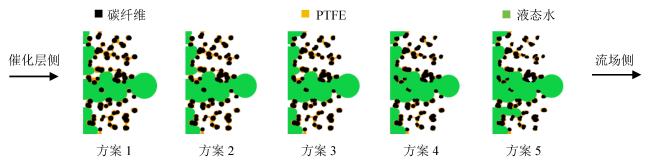
Table 1 Design of conventional diffusion layer and gradient diffusion layer with PTFE content of 10%表1 聚四氟乙烯含量为10%的常规扩散层及梯度化扩散层设计 |
| 设计 | 方案编号 | 聚四氟乙烯分布含量/% |
|---|---|---|
| 常规扩散层 | 1 ~ 5 | 10(均匀分布) |
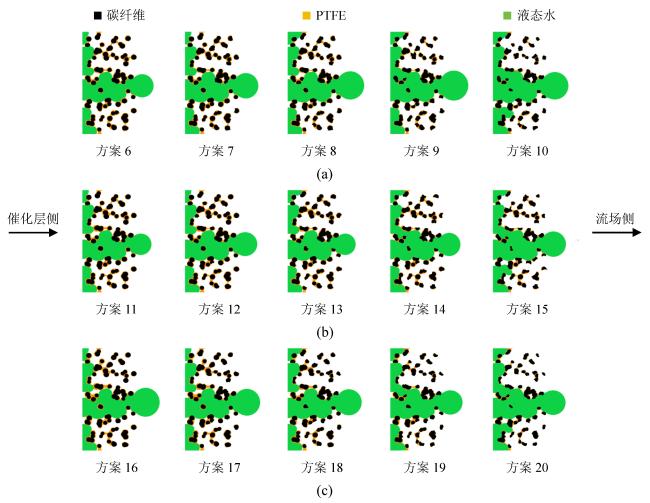
| 双梯度扩散层 | 6 ~ 10 | 12(进口);8(出口) |
| 11 ~ 15 | 14(进口);6(出口) | |
| 16 ~ 20 | 16(进口);4(出口) | |
| 三梯度扩散层 | 21 ~ 25 | 12(进口);10(中间);8(出口) |
| 26 ~ 30 | 14(进口);10(中间);6(出口) | |
| 31 ~ 35 | 16(进口);10(中间);4(出口) |
2 数值模型
2.1 控制方程
2.2 格子玻尔兹曼方法验证
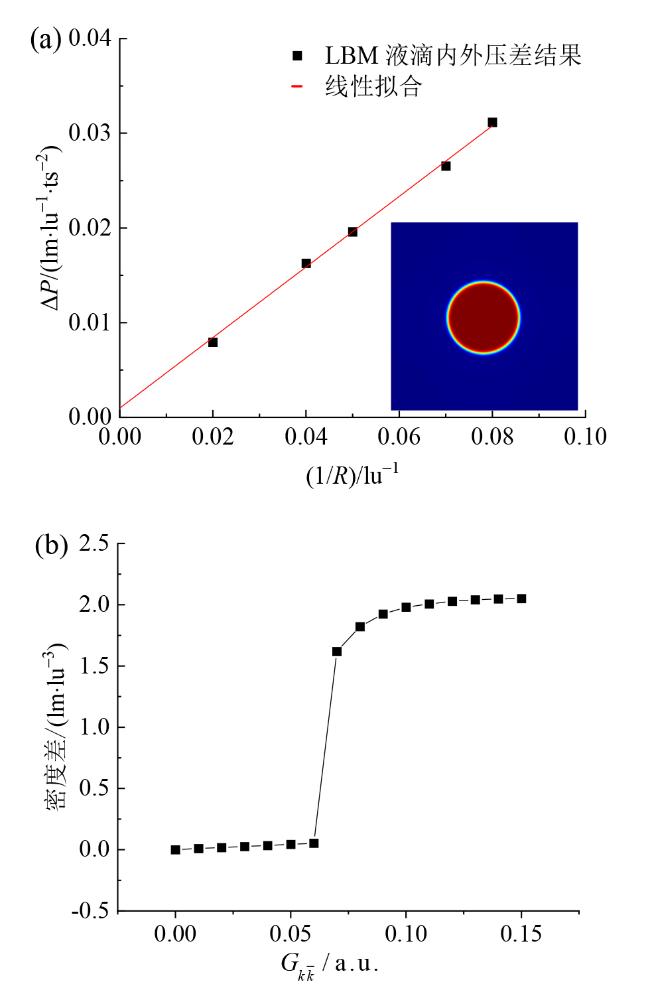
Fig. 2 Laplace's test: (a) the relationship between the pressure difference inside and outside the droplet and the reciprocal radius of the droplet; (b) the difference between the maximum and minimum density of gas with different ${{G}_{k\bar{k}}}$values图2 拉普拉斯验证:(a)液滴内外压差与液滴半径倒数之间的关系;(b)不同${{G}_{k\bar{k}}}$值的气体最大密度和最小密度之间的差异变化 |
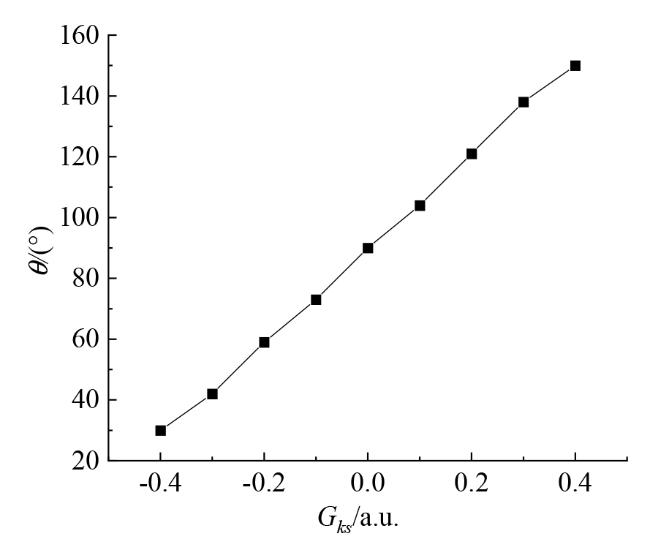
Fig. 3 Change curve of static contact angle with Gks图3 静态接触角随Gks的变化曲线 |
3 结果与分析
3.1 聚四氟乙烯双梯度的扩散层
Fig. 5 Two-phase flow of polytetrafluoroethylene with double gradient distribution of diffusion layers with different aging degrees图5 聚四氟乙烯双梯度分布的扩散层不同老化程度的气液两相流形态 |
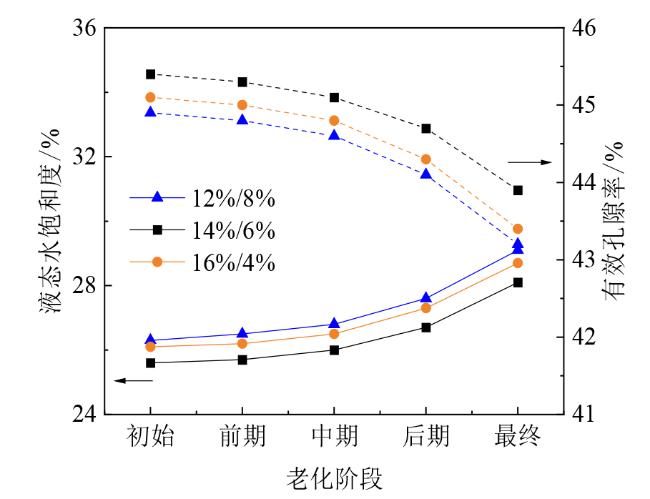
Fig. 6 Liquid saturation and effective porosity curves of double gradient diffusion layers with different aging degrees图6 双梯度扩散层不同老化程度下液态水饱和度和有效孔隙度曲线 |
3.2 聚四氟乙烯三梯度的扩散层
Fig. 7 Two-phase flow of polytetrafluoroethylene diffusion layers with different aging degrees in three gradient distribution图7 聚四氟乙烯三梯度分布的扩散层不同老化程度的气液两相流形态 |
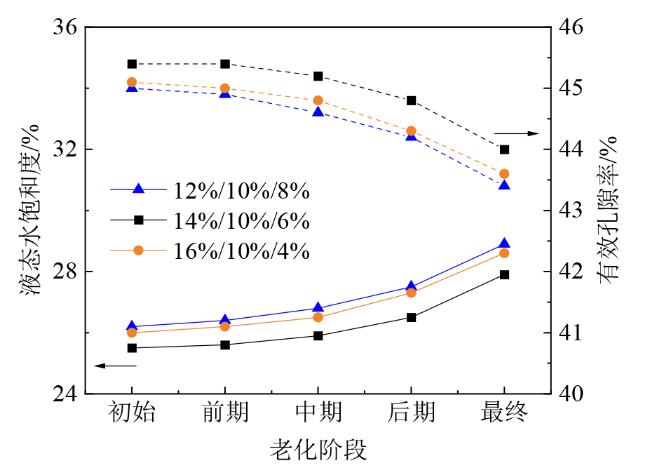
Fig. 8 Liquid saturation and effective porosity curves of three gradient diffusion layers with different aging degrees图8 三梯度扩散层不同老化程度下的液态水饱和度和有效孔隙度曲线 |